Image by For the test, you’ll be given a scenario and then asked to choose which one of these four types to use. Questions on Storage Gateway are very likely to come up in the exam, but even a basic understanding should be enough to help you ace these questions. The important thing is being able to tell them apart. I’m going to make this simpler to understand by comparing each option to something you already know.
Brief Description of Storage Gateway
This is the official AWS description of Storage Gateway: Official descriptions like this can be confusing at first. But let’s break it down:
It’s a storage service It’s for hybrid storage (hybrid meaning both on-premises and cloud) It’s for use on-premises It gives you virtually unlimited cloud storage
Types of Gateway Storage
There are three types of storage in Storage Gateway: For the exam though, you need to know the difference between four options and learn five different terms because Volume Gateway offers two additional options:
Cached Volumes Stored Volumes
All this terminology is what makes learning Storage Gateway so confusing.
File Gateway
The easiest way to understand the definition of a File Server is to think of a mailbox on a street corner. Any individual or business can drop their mail into that single mailbox. It will be filled with letters and packages from lots of different people. A File Server is like that mailbox. It’s a central computer that lots of other computers (the people mailing letters) can connect to. File Servers are useful for collaboration. Let’s imagine a File Server called MyFileServer. Bob using Laptop A saves a document called BusinessPlan.docx to MyFileServer. Later, Jane using Laptop B accesses BusinessPlan.docx and make changes to it. Priyanka using Laptop C checks BusinessPlan.docx the next day to make sure it’s accurate.
A Brief Description of File Gateway
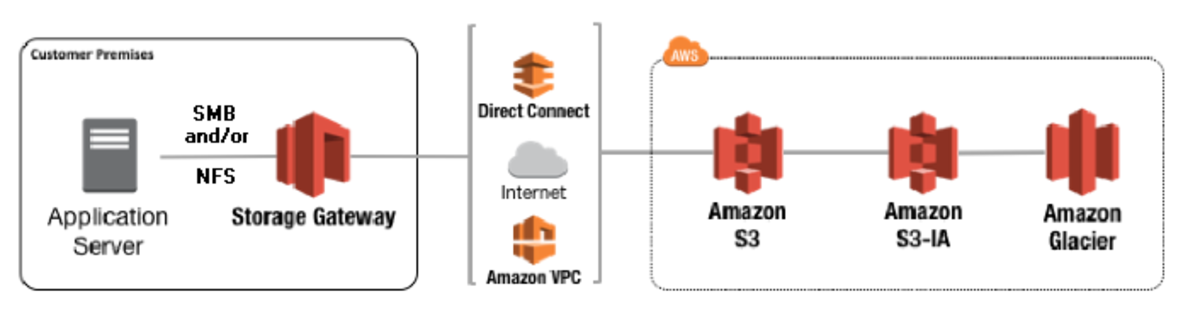
Here is the AWS description of File Gateway: Think of File Gateway as a File Server in the cloud. In this case, files are stored in S3. For your exam, remember that it uses Network File System (NFS) and Server Message Block (SMB). If a question asks about File storage in relation to Storage Gateway, or mentions NFS or SMB, the answer is most likely File Gateway.
Tape Gateway
Tape Gateway deals with backups. Before the cloud and Network Attached Storage (NAS) devices, tapes were used to back up servers. https://docs.aws.amazon.com/storagegateway/latest/userguide/StorageGatewayConcepts.html Think of Tape Gateway as storing the contents of physical backup tapes with data backed up into either S3, Glacier, or Glacier Deep Archive. On the exam, if you see a question related to Storage Gateway and tapes, Tape Gateway is a likely answer.
Volume Gateway
When a question asks about file storage, NFS or SMB, think File Gateway. When a question asks about backup tapes, think Tape Gateway. When a question asks about iSCSI (Internet Small Computer System Interface), think Volume Gateway. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tape_drive#/media/File:Dds_tape_drive_01.jpg
A Brief Description of Volume Gateway
Here is an AWS description: What makes Volume Gateway confusing is that, as I mentioned before, it comes in two different types: Stored and Cached.
Stored Volumes
The easiest way to understand Stored Volumes is to think of a smartphone. Smartphones generally back up everything into the cloud. An iPhone will back up data into iCloud. An iPhone user generally doesn’t interact with iCloud for day-to-day usage. What they use, Contacts, eBooks, or downloaded music, is mostly on their phone. But if they upgrade their phone, they can log into their account on the new phone, and then their data like Contacts will download to their new phone. They can also download photos, documents, etc. to the new phone. Stored Volumes are similar in that all data is stored on-premises. Users accessing that data are accessing it on-premises. The data going into the AWS cloud is for backup purposes.
A Brief Description of Stored Volumes
Here is how AWS describes it: Stored Volumes are designed for disaster recovery. If an on-premises storage device becomes corrupted, that data can then be accessed from S3.
Cached Volumes
For Cached Volumes, think of a Chromebook. A Chromebook is a laptop with limited local storage. It’s designed for use with cloud-based services like Gmail, YouTube, and Google Docs. Instead of downloading software, a Chromebook uses Android apps.
A Brief Description of Cached Volumes
Cached Volumes are similar in that most data is stored in AWS S3. Only data that’s used frequently is stored (or cached) on-premises. Just like a Chromebook doesn’t need much local storage, using Cached Volumes doesn’t require as much on-premises storage.
Study Points to Remember
Keep these key Storage Gateway points in mind when you are taking your exam.
Volume Gateway
For your exam, remember that Stored Volumes store all data both on-premises and in the cloud. Data is backed up largely for Disaster Recovery (DR) if on-premises storage is no longer available for some reason. All data is kept on-premises. Cached Volumes store all data in the cloud. Only frequently accessed data is kept on-premises. For the exam, pay attention to the scenario in each question. If data is being stored and used on-premises but backed up into the cloud, that’s Stored Volumes. If a company wants to minimize on-premises storage costs by storing only frequently accessed data while keeping everything else in the cloud, that’s Cached Volumes.
Tape Gateway
Tape Gateway is a virtualized version of physical tape cartridges.
File Gateway
File Gateway uses the NFS or SMB protocols. Look for the word ‘file’ in an exam question.
References
I’ve deliberately simplified this information to make it easy to understand. You should read the following before you take your exam to get a more in-depth description of each option: This content is accurate and true to the best of the author’s knowledge and is not meant to substitute for formal and individualized advice from a qualified professional. © 2020 LT Wright